Phishing used to be easy to spot: poorly written emails, broken English, and fake links you could catch from a mile away. Now? Not so much. We’ve officially entered the era of deepfake phishing — where scammers don’t just send a suspicious message… they make it look real.
Your boss.
Your colleague.
Your partner.
Even your mom.
And that’s where it gets scary.
The question is no longer “Is this link suspicious?”
It’s “How do I even know this person is real?”
Welcome to the new reality. Here’s how to know when something is a scam in this deepfake-driven world.
What Exactly Is Deepfake Phishing?
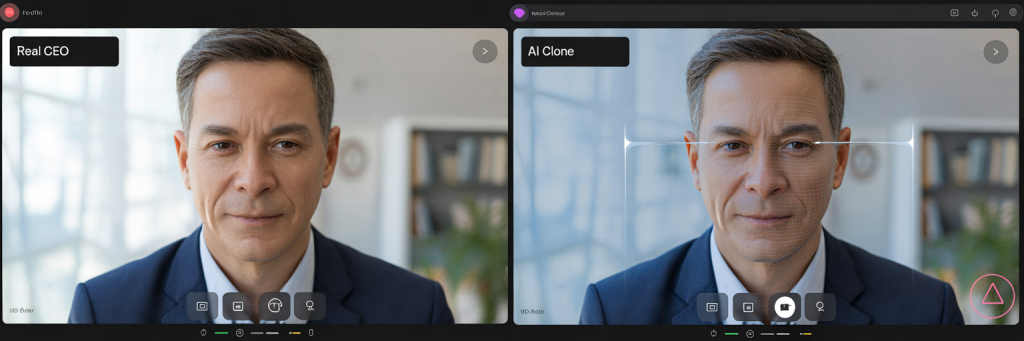
Deepfake phishing is what happens when old-school scams get a 2026 upgrade. Scammers use AI to clone someone’s face or voice and then use that identity to trick you into doing something you normally wouldn’t — sending money, sharing credentials, approving a sensitive request, or just panicking. This is the foundation of modern AI voice cloning scams and deepfake video scams.
Imagine getting a video call from your “CEO” telling you to urgently transfer funds.
Or a voice note from your friend asking for your bank details.
Or a quick “Hey, can you open this link?” from someone who looks exactly like your coworker.
This is deepfake phishing. And you need to be aware of it. According to recent warnings issued by the FBI, deepfake-enabled scams are expected to rise throughout 2026.
For a broader look at how generative AI is revolutionizing scams beyond video and voice — including AI-crafted emails and automated spear-phishing — see our earlier analysis on PhishGPT and the rise of AI phishing attacks.
How Deepfake Phishing Works

Deepfake phishing feels real — and it’s designed to make you react fast. Understanding how AI phishing attacks operate helps you spot the red flags early. Here’s how scammers pull it off:
1. They use public photos, videos, and audio to clone someone.
Anything posted online is fair game: interviews, IG stories, YouTube clips. This is how AI voice cloning scams usually begin—by scraping your public content to mimic your tone and speech patterns.
How to know it’s fake:
If the person suddenly sounds too perfect, overly smooth, or slightly robotic, be cautious. AI often removes natural quirks.
2. They create a fake video or audio message that looks legitimate.
AI tools can mimic facial expressions, lip movements, tone, and timing. This is the basis of most deepfake video scams today.
How to know:
Look for glitches, unnatural blinking, off timing, or audio that feels too clean.
3. They make everything urgent.
“Do this now.”
“This is urgent.”
“Don’t tell anyone.”
Urgency is the psychological weapon behind nearly all AI-powered phishing attacks.
How to know:
Real colleagues don’t pressure you through surprise video calls to break process.
4. They use trusted platforms.
Emails, Slack, WhatsApp, Zoom — everything is possible. Most AI phishing attacks succeed because the fake identity shows up in a familiar place.
How to know:
If someone reaches out in a way they normally don’t, pause. Scammers rely on catching you off guard.
CISA has published detailed guidance on how attackers use AI to conduct highly convincing impersonations.
Real Stories and Statistics That Prove This Is Already Happening

- Employees have approved huge wire transfers after joining video calls with a “CEO” who was a deepfake.
- 70% of people said they aren’t confident they can tell the difference between a real and cloned voice.
- Scammers have impersonated celebrities to promote fake investments.
- Companies have been tricked by voice clones requesting confidential data.
- CEO fraud now targets at least 400 companies per day.
- Deepfake content exploded from 500K in 2023 to 8M by 2025.
These are not hypothetical scenarios. They’ve already happened to real people in real companies. Cybercrime reports from Europol also confirm that deepfakes are now being used in high-value financial fraud cases.
How to Know It’s a Deepfake Scam — Your Checklist
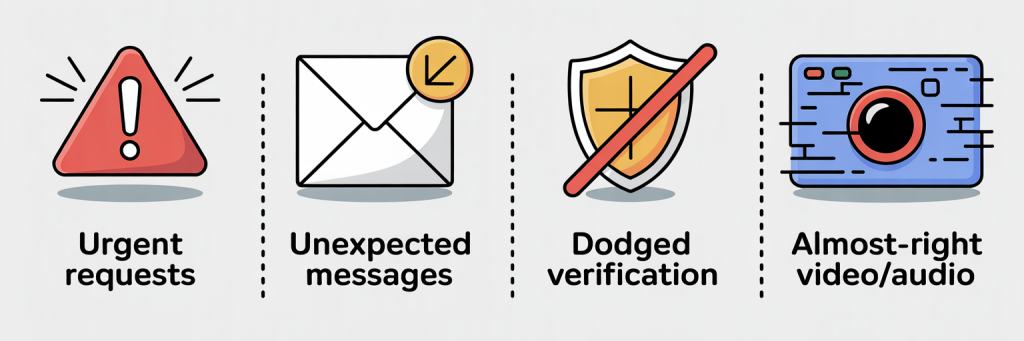
Here’s your survival kit for spotting deepfake phishing before they hit you:
✔ The request breaks normal process.
✔ The person refuses to verify identity on another channel.
✔ The audio or video is “almost right” but slightly off.
✔ The message feels urgent, secretive, or unusual.
✔ You receive an unexpected request out of nowhere.
If even one of these is true — stop and verify.
How to Act Properly Against Deepfake Scams

Verify via a second channel — call or message the real person separately.
Take your time — most AI phishing attacks rely on rushing you
Limit what you post online — fewer materials = fewer cloning opportunities.
Educate your team — deepfake phishing is most dangerous when only one person knows about it.
Enforce strong approval processes — scams fail when process wins.
Final Thought
Deepfake phishing is a new kind of scam — one that looks real and sounds real. In business, these deepfake phishing techniques are now fueling a new wave of CEO fraud scams that look completely legitimate.
But with the right mindset, and by knowing what signs to look for, you can spot it before it hits.
Because in the age of deepfake phishing, the real skill isn’t just avoiding suspicious links…
It’s knowing whether the person talking to you is even a real person at all.



